Transformer (Transformer) is the use of the principle of electromagnetic induction to change the AC voltage device, the main components are the primary coil, secondary coil and iron core (core). The main functions are: voltage conversion, current conversion, impedance conversion, isolation, voltage stabilization (magnetic saturation transformer) and so on.
How does a transformer work?
The working principle of a transformer is based on electromagnetic induction. When the current in the main coil varies, it produces an alternating magnetic field which is conducted through the iron core into the secondary coil. According to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, a change in the magnetic field in the secondary coil causes an induction of voltage. If the number of turns on the secondary coil is more than the number of turns on the primary coil, then the output voltage will be higher than the input voltage; if the number of turns on the secondary coil is less than that on the primary coil, then the output voltage will be lower than the input voltage.
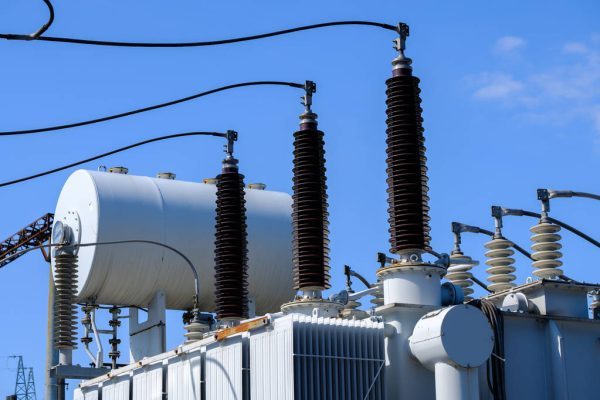

Isolators and transformers at the electrical substation. Electrical equipment
What are the transformer categories?
Transformers can be categorized into two types: step-up transformers and step-down transformers. A step-up transformer is used to increase the input voltage to the desired output voltage, while a step-down transformer reduces the input voltage to the desired output voltage. The magnitude of the output voltage depends on the ratio of turns in the main and secondary coils.
Transformers are very efficient, often reaching over 90%. This means that it can transfer power from one circuit to another in an efficient manner with little energy loss.
In addition to its step-up and step-down functions, a transformer also serves to isolate the input and output circuits. Through the iron core, the transformer is able to prevent high voltage or high frequency currents from being passed to the secondary coil or input circuit, thus providing a degree of electrical isolation and safety.
In the home, the electricity supply is usually AC, and different appliances and equipment may require different voltages for proper operation. For example, some devices may require a lower voltage, such as televisions, stereo systems, computers, etc., while certain devices may require a higher voltage, such as refrigerators, washing machines, hair dryers, etc.
The purpose of a household transformer is to step up or step down the voltage of a power supply to meet the voltage needs of different devices. They are usually small, portable devices that can be plugged into a home power outlet and provide a supply of electricity at the proper voltage through an output port for use by the device.
Characteristics of household transformers include:Input and output voltages:The input voltage of a household transformer usually matches the local grid voltage, such as 110 V or 220 V. The output voltage can be adjusted according to the needs of different devices, with common output voltages such as 12 V, 24 V, 110 V or 220 V. The output voltage can be adjusted according to the needs of different devices.
Power capacity: household transformers have a certain power capacity, which indicates the maximum power output they can provide. Power capacity is usually expressed in watts (W) units, such as 100W, 200W, etc.. Users in the selection of household transformers should be based on the power requirements of the equipment to choose the appropriate capacity.
Sockets and Connectors: Household transformers usually have multiple output sockets or connectors for connecting multiple devices. These sockets may adopt different power standards, such as European standards, American standards, etc., in order to adapt to the equipment in different regions.
Safety protection: Household transformers usually have safety features such as overload protection, overheating protection and short-circuit protection to ensure the safe operation of the transformer and equipment.
It should be noted that household transformers can only be used for small power appliances and equipment, such as cell phone chargers, computer adapters, small appliances and so on. For high power equipment such as air conditioners, electric furnaces, etc., you need to use a special high power transformer or take other voltage conversion.
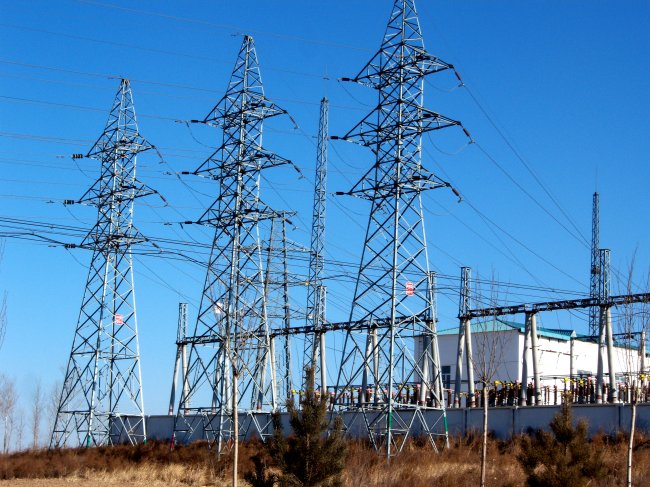

Transformers play an important role in power systems. They are used to transform the voltage in transmission lines in order to transfer power between different voltage levels. Transformers are also widely used in electronic equipment, industrial equipment and household power for adapting to the voltage requirements of different equipment.
Enameled wire is widely used in transformers mainly because of its key properties such as insulation, high temperature resistance, uniform insulation thickness, coil compactness and electrical conductivity, which ensure safe operation and efficient energy transmission.
In summary, a transformer is an electrical device based on the principle of electromagnetic induction and is used to change the voltage of alternating current. It functions as a step-up, step-down and isolation circuit and plays an important role in power systems and various electrical devices.